Why PAES?
Educators of students with special needs are required to identify appropriate and measurable postsecondary goals based on age-appropriate transition assessments related to training, education, employment, and independent living.
1.
A Valid Data-Driven Transition Assessment
Persons responsible for developing transition plans need valid data-driven assessments that provide guidance in identifying post-high outcomes and employment potential.
2.
An Assessment of Employment Potential
The PAES assessment gives clear and definitive answers to these questions by providing a profile of job performance and workplace skills that generalize to the expectations of a variety of employment options.
3.
A Staff Development Tool
“Because the pre-service preparation of teachers and administrators in assessment and data analysis has been weak or nonexistent, educators must have generous opportunities to acquire knowledge and skills related to formative classroom assessment, data collection, data analysis, and data-driven planning and evaluation.”
- National Staff Development Center
PAES Suits a wide range of ages and abilities and is customizable to a student’s level of need
Who participates in the PAES Lab?
The PAES lab serves students who have learning disabilities, mild to moderate cognitive disabilities, hearing loss, physical disabilities, developmental and multiple disabilities.
Higher functioning students tend to move quickly through the PAES jobs to explore and identify their strengths and interests.
Students with more significant cognitive and physical challenges identify their strengths and needs by performing as many whole PAES jobs as possible followed by discovering which subtasks of other jobs can be performed. If Accommodations or Modifications are necessary, PAES documents the necessary supports.
“If you’re conscious and can move any part of your body, you are employable” - Dr. Lou Brown, Emeritus Professor, University of Wisconsin
WHERE IS PAES USED?
IDEA requires that beginning not later than age 16 students’ IEPs must have appropriate measurable postsecondary goals based on age-appropriate transition assessments.
Some states require that postsecondary goals are identified and transition services initiated not later than age 14.
Consequently, PAES labs are typically located in middle schools and high schools.
Other locations include community colleges and special needs adult services.
How does PAES Work?
Mimics Real Workplace Settings
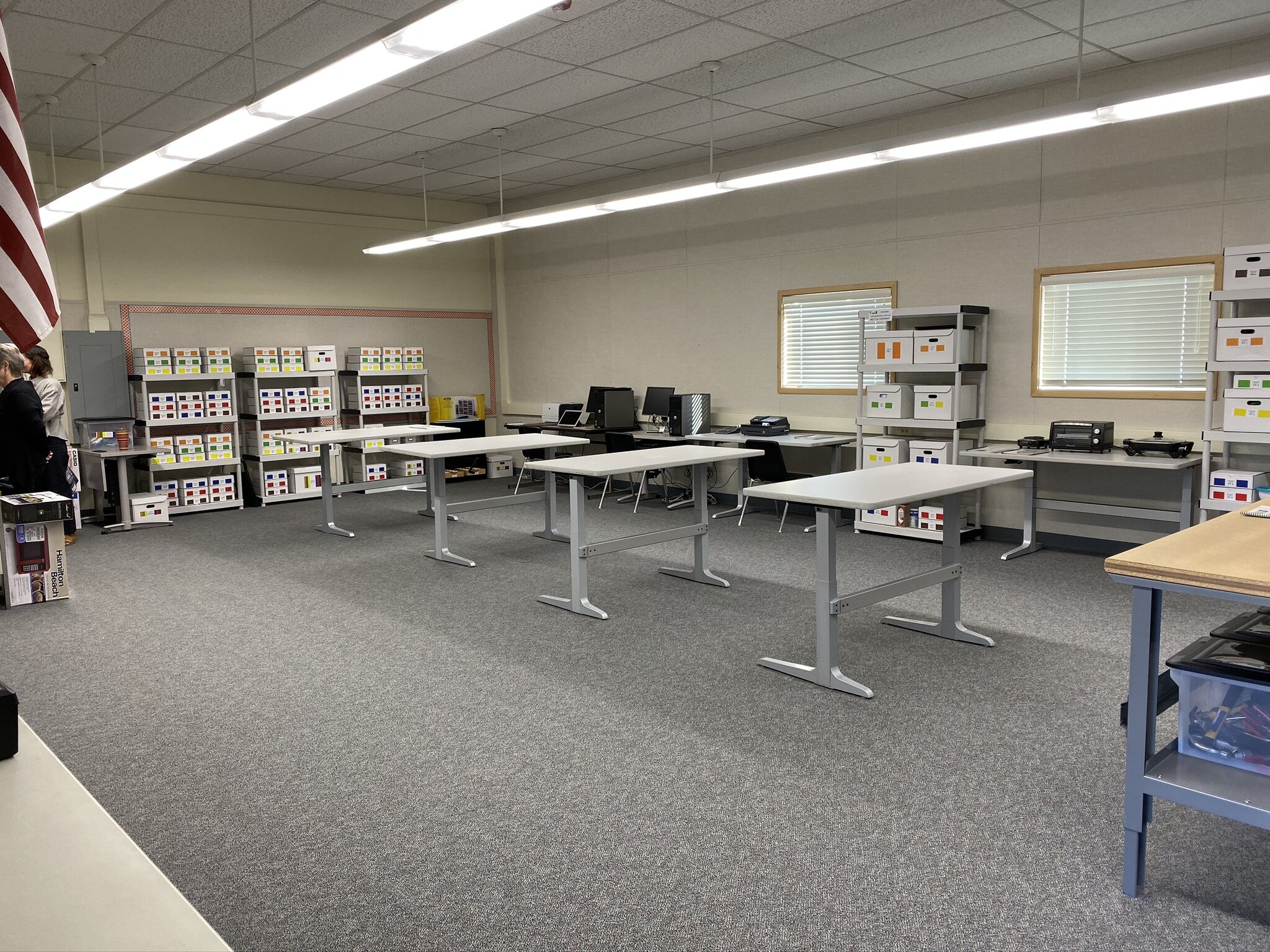
The PAES Lab is designed to be as much like a real workplace as possible.
Teachers become Supervisors, and Students become Employees
Employees Clock In/Clock Out, just like a real job
Employees follow an independent work procedure, which guides them through the process of getting their own job materials and calling for supervisors only when necessary
Career Exploration
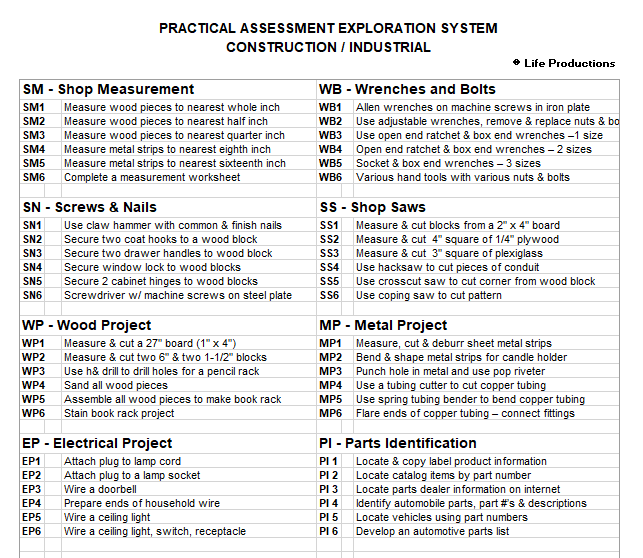
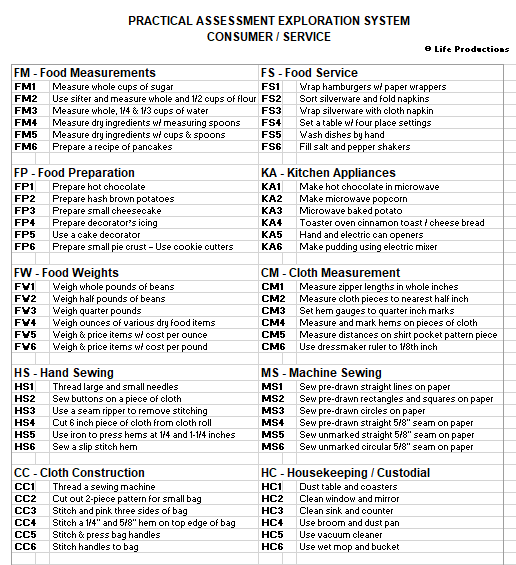
In this Vocational Assessment, individuals explore jobs in five components, typical to community based employment, to determine their interests and abilities. Employees first complete a "Baseline Assessment" of the most-basic, Level 1 jobs (orange) to determine their areas of interest and ability. Then, they explore more difficult jobs in their areas of strength. By the time employees attempt Level 6 (brown) jobs, they are competing at the level of average entry level jobs in the community.
PAES has 5 components:
Within each component, there are 8-10 job units
Each job unit has 6 levels of difficulty (from orange to brown)
Click on each item below to see more:
PREDICTS EMPLOYMENT POTENTIAL WITH DATA DRIVEN RESULTS
Assesses Employees on Criteria Real Employers Want to Know:
Assistance Required
Interest in the Job
Quality of the Work
Work Rate
Number of Attempts Required
PAES is Validated to predict employment potential 3 to 5 years in the future. The Predictive Validity Study, published in the Educational Measurement Journal*, compared the predictive capability of the PAES and two standardized aptitude tests (CAPS* & DAT*) for predicting student work performance 3 to 5 years later. PAES scores were strongly related to amount of assistance needed on a job and were significantly related to wages and hours worked. Career Ability Placement Survey (CAPS) and Differential Aptitude Test (DAT) scores were very weakly related to work performance
TRACKS WORKPLACE "SOFT" SKILLS & REWARDS APPROPRIATE WORKPLACE BEHAVIORS
In addition to their Aptitude for specific job skills, PAES Employees are assessed for 30 Workplace soft skills, such as the following:
Hygiene
Communication Skills
Staying on Task & Following Directions
Frustration Tolerance
Reactions to Non-Preferred Work
Interacting with Supervisors and Other Employees
Safety
Employees are rewarded points for completing jobs and for appropriate workplace behaviors and lets supervisors customize rewards systems to mimic real world compensation.
*“An Empirical Study Comparing Curriculum-Embedded Assessment and Traditional Aptitude Measures for Predicting Job-Related Outcomes for Students with Disabilities” Educational Measurement, 5(1), 57-70.]